构建和发现结构与功能之间的关系是自然科学研究的关键课题,而动力学过程与机制的研究在其中起着极为重要的作用;从对传统的体相和均相宏观静态过程的观测发展到在低维空间尺度和超快时间分辩上对非均相体系和动态过程的捕捉已经成为基础研究的主要趋势。本课题组主要以光子学成像及超快光谱为主要技术和基础,旨在单分子水平和动力学上研究低维结构及大分子等体系的功能特性和机制,在微观和动力学上揭示结构和功能之间的关系。
研究方向
¨光控自组装结构及功能
从分子和结构设计出发,合成具有光响应的有机分子,利用外部刺激调控其自组装结构、功能和性质,揭示结构和功能之间的关系和机制,探索获得可控自组装功能材料和器件的新途径。
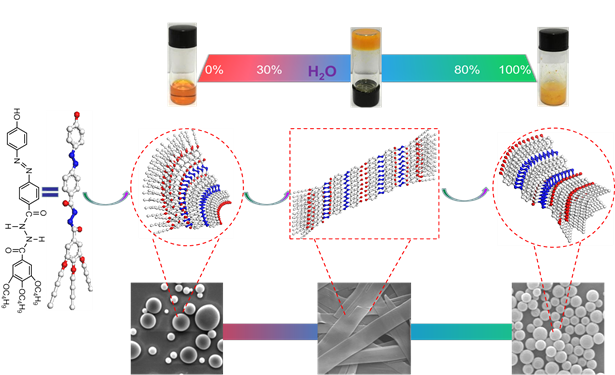
Fig.1. Water regulated self-assembly behavior and mechanism of BNB-t4.
¨低维结构光物理与光化学
主要利用单分子/颗粒及瞬态光谱技术实时、原位研究半导体低维结构体系中的光物理与光化学过程及机制,包括光催化、光敏化、增强发光、能量传递、电子转移等。
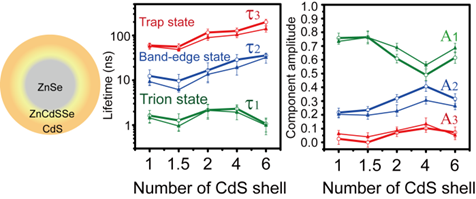
Fig. 2. Shell-dependent blinking behavior and dynamics of single quantum dots
¨生物大分子动态学
旨在从生物大分子动态学上揭示生命体中蛋白结构与功能之间关系的科学本质。主要利用单分子荧光示踪及瞬态光谱探测技术实时研究蛋白相互作用过程、酶反应过程、大分子的输运及运动性、表面-界面的蛋白动态学过程等。
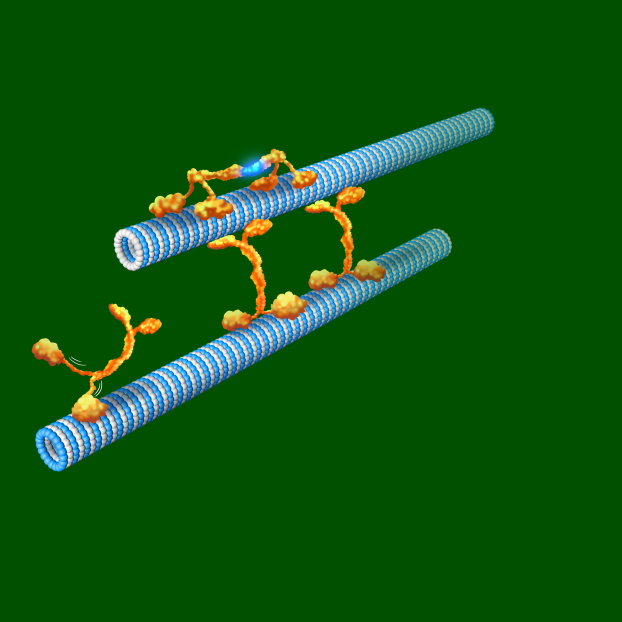
Fig. 3 Single-molecule observations on the motility and behavior of Kinesin on microtubule.
主要研究条件
本课题组主要的研究设备和条件包括:单分子多通道全内反射荧光显微镜(sm-TIRFM, Nikon),单分子荧光寿命成像(FLIM,Olympus、Picoquant)、单分子AFM-Raman联用系统(NT-MDT)、宽带调谐飞秒激光器(Coherent)+皮秒分辨TCSPC、飞秒激光放大器系统、飞秒瞬态吸收光谱仪等。以及外-可见-近红外分光光度计(Cary 5000)、稳态/瞬态荧光光谱仪(FLS 980)、光谱型椭圆偏振仪(Woollam)、动态光散射粒度仪、细胞培养和蛋白纯化等常规测试设备。
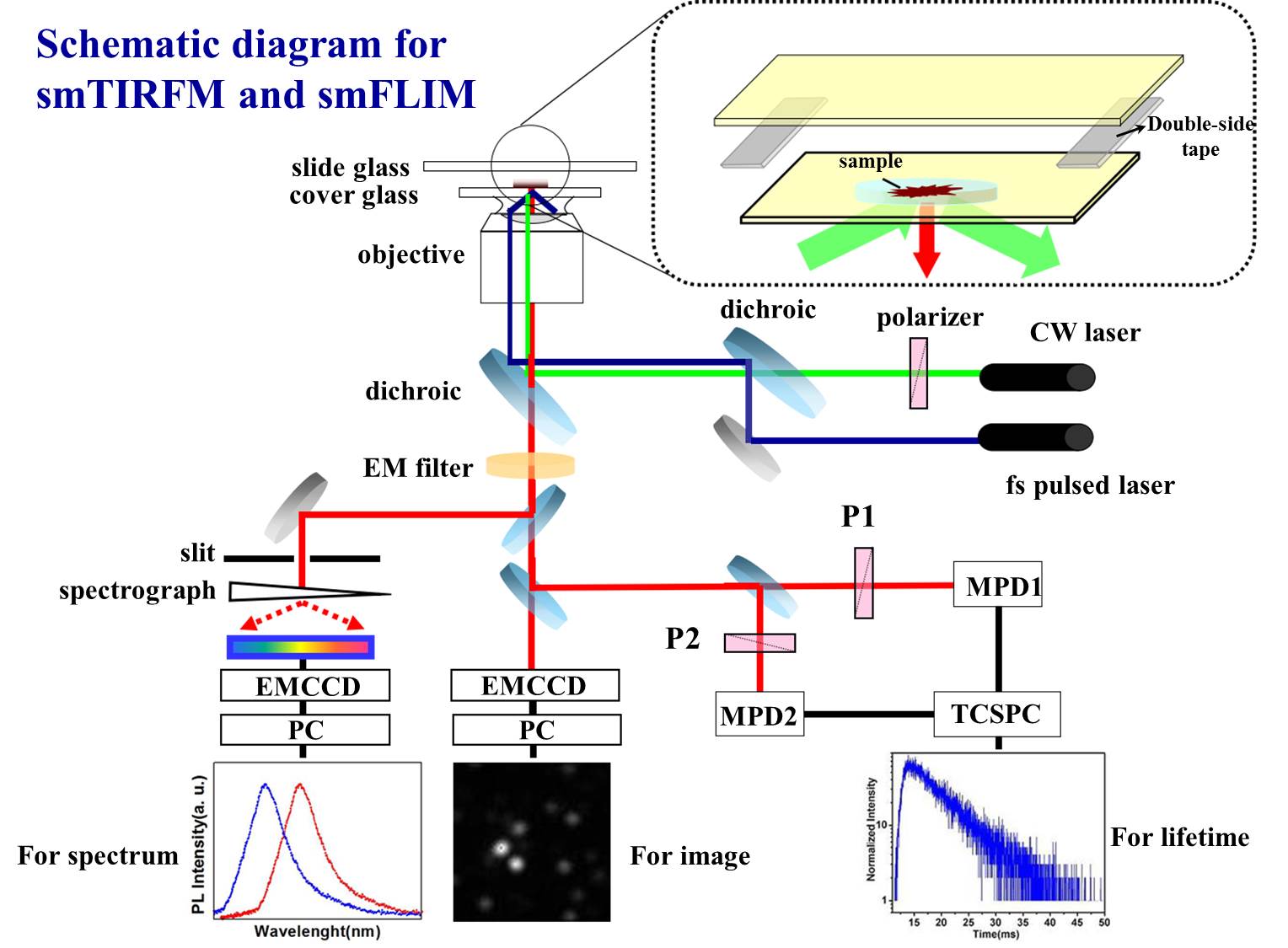
Fig. 4. Schematic diagram of smTIRFM and smFLIM
近年发表的部分论文
1.Xing Guo, Yanmin Kuang*, Sheng Wang, Zhaohan Li, Huaibin Shen and Lijun Guo*, Shell-dependent blinking behavior and fluorescence dynamics of single ZnSe/CdS core/shell quantum dots, Nanoscale, 2018, 10, 18696-18705.
2. Pan Wang, Kuo-Fu Tseng, Yuan Gao, Michael Cianfrocco, Lijun Guo, Weihong Qiu*, The Central Stalk Determines the Motility of Mitotic Kinesin-14 Homodimers, Current Biology, 2018, 28(14): 2302–2308.
3. Liu He, Xia Ran,* Jinxing Li, Qiongqiong Gao, Yanmin Kuang and Lijun Guo*, A highly transparent and autonomic self-healing organogel from solvent regulation based on hydrazide derivatives, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018, 6, 16600–16609.
4. Kuo-Fu Tseng, Pan Wang, Yuh-Ru Julie Lee, Joel Bowen, Allison M. Gicking, Lijun Guo, Bo Liu and Weihong Qiu*, The preprophase band-associated kinesin-14 OsKCH2 is a processive minus-end-directed microtubule motor, Nature Communications, 2018, 9:1067
5. Xia Ran, Qiongqiong Gao, Yu Zhang* and Lijun Guo*, Colorimetry and phase transition characteristics in sensing fluoride anion based on hydrazide organogelators, RSC Adv., 2017, 7, 56016-56022.
6. Qiongqiong Gao, Liu He, Yajie Li, Xia Ran* and Lijun Guo*, Controllable wettability and adhesion of superhydrophobic self-assembled surfaces based on a novel azobenzene derivative, RSC Adv., 2017, 7, 50403–50409.
7. Zhen Chi, Xia Ran*, Lili Shi, Jie Lou, Yanmin Kuang, Lijun Guo*, Molecular Characteristics of a Fluorescent Chemosensor for the Recognition of Ferric Ion Based on Photoresponsive Azobenzene Derivative, Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2017,171: 25–30.
8. Beibei Xu, Xiaojuan Wang, Chaofeng Zhu, Xia Ran, Tianfeng Li* and Lijun Guo*, Probing the inhomogeneity and intermediates in the photosensitized degradation of rhodamine B by Ag3PO4 nanoparticles from an ensemble to a single molecule approach, RSC Adv., 2017, 7, 40896-40905.
9. Qiuyue Li, Zhen Chi, Tianfeng Li, Xia Ran* and Lijun Guo*, Photoresponsive behavior and switchable nonlinear optical properties of Langmuir-Blodgett film based on azobenzene derivatives, Optical Express, 2017, 25(10): 11503-11513
10. Xia Ran, Yajie Li, Qiongqiong Gao, Weihong Qiu* and Lijun Guo*, A Smart Phase-Selective Gelator for Recycling Aromatic Solvents, the Removal of Toxic Dyes, and Molecular Delivery, Asian J. Org. Chem. 2017, 6: 95-101.
11. Yajie Li, Xia Ran*, Qiuyue Li, Qiongqiong Gao and Lijun Guo*, Water-regulated self-assembly structure transformation and gelation behavior prediction based on a hydrazide derivative, Chem. Asian J., 2016, 11, 2157-2166.(cover page)
12. Xia Ran, Kun Zhang, Lili Shi, Zhen Chi, Weihong Qiu* and Lijun Guo*, Single-step fabrication of large-scale patterned honeycomb structures via self-assembly of a small organic molecule, RSC Advances, 2015, 5, 60518-60523.
13. Lili Shi, Xia Ran* (co-first author), Yajie Li, Qiuyue Li, Weihong Qiu, and Lijun Guo*, Photoresponsive Structure Transformation and Emission Enhancement Based on a Tapered Azobenzene Gelator, RSC Advances, 2015, 5, 38283-38289.
14. Xia Ran, Haitao Wang, Lili Shi, Jie Lou, Bo Liu, Min Li and Lijun Guo*, Light-driven Fluorescence Enhancement and Self-assembled Structural Evolution of an Azobenzene Derivative, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2014, 2, 9866-9873.
15. Xia Ran, Haitao Wang, Jie Lou, Lili Shi, Bo Liu, Min Li, and Lijun Guo*, Morphology and Wettability Tunable Organogel System Based on An 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Derivative, Soft Materials, 2014, 12, 396–402.
16. Tianfeng Li, Lizhen Gao, Wen Lei, Lijun Guo*, Huayong Pan, Tao Yang, Yonghai Chen and Zhanguo Wang, InAs-mediated Growth of Vertical InSb Nanowires on Si Substrates, Nanoscale Research Letters, 2013, 8:333.
17. Tianfeng Li, Lizhen Gao, Wen Lei, Lijun Guo*, Tao Yang, Yonghai Chen and Zhanguo Wang, Raman Study on Zinc-blende Single InAs Nanowire Grown on Si (111) Substrate, Nanoscale Research Letters, 2013, 8:27.
18. Suraj Saraswat, Anil Desireddy, Desheng Zheng, Lijun Guo, H. Peter Lu, Terry P. Bigioni, and Dragan Isailovic*,Energy Transfer from Fluorescent Proteins to Metal Nanoparticles,J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115 (35): 17587–17593.
19. Lijun Guo, Yuanmin Wang, H. Peter Lu*, Combined Single-Molecule Photon-Stamping Spectroscopy and Femtosecond Transient Absorption Spectroscopy Studies of Interfacial Electron Transfer Dynamics, J. Am. Chem. Soc.; 2010,132(6):1999-2004 (cover page.
20. Chih-Wei Chang, Lijun Guo, Ya-Ting Kao, Jiang Li, Chuang Tan, Tanping Li, Chaitanya Saxena, Zheyun Liu, Lijuan Wang, Aziz Sancar and Dongping Zhong*, Ultrafast Solvation Dynamics at Binding and Active Sites of Photolyases, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2010, 107(7):2914-2919.
21. C.-W. Chang, T.-F. He, L. Guo, J. A. Stevens, T. Li, L. Wang and D. Zhong*, Mapping Solvation Dynamics at the Function Site of Flavodoxin in Three Redox States. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132:12741-12747.